Robot Calibration app benefits

Accurate calibration of the tool center point (TCP)

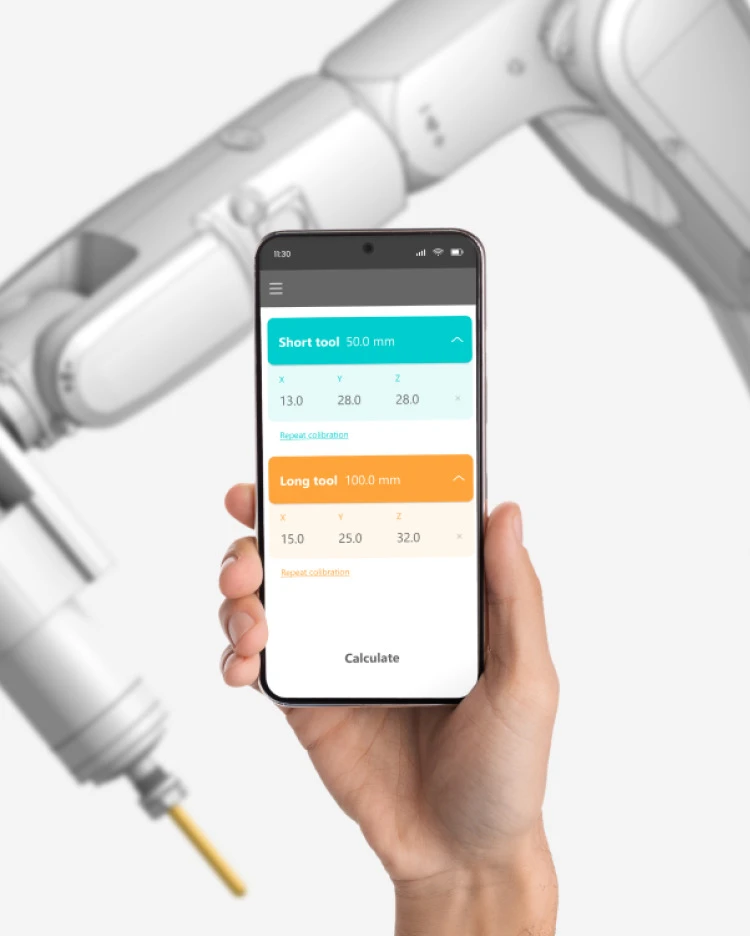
Use of the double-spike method

Automatic data transfer to MachineMaker and SprutCAM X

Elimination of errors caused by manual data entry

Reduced robot debugging time

Elimination of costly calibration tools or services

Ever-growing list of supported robots and mechanisms

The engineer interacts with the robot using a standard smartphone
How the Robot Calibration app works
Step 1
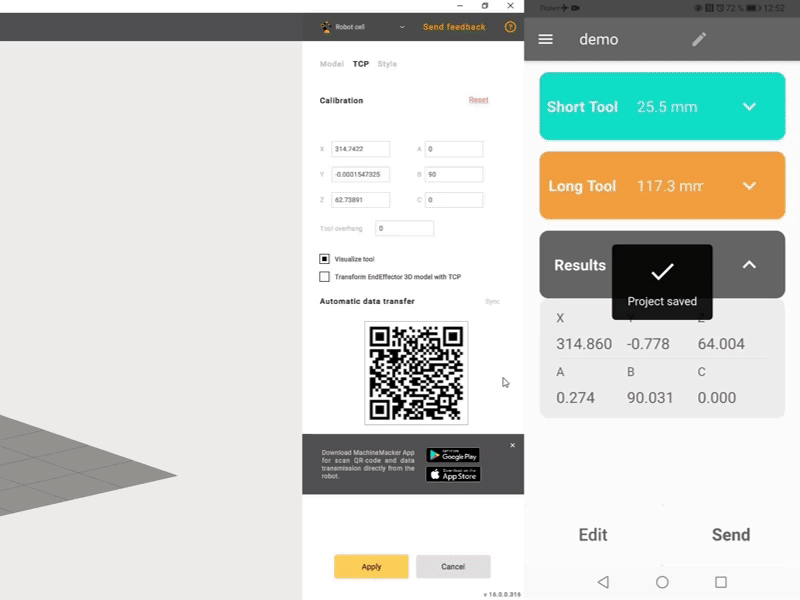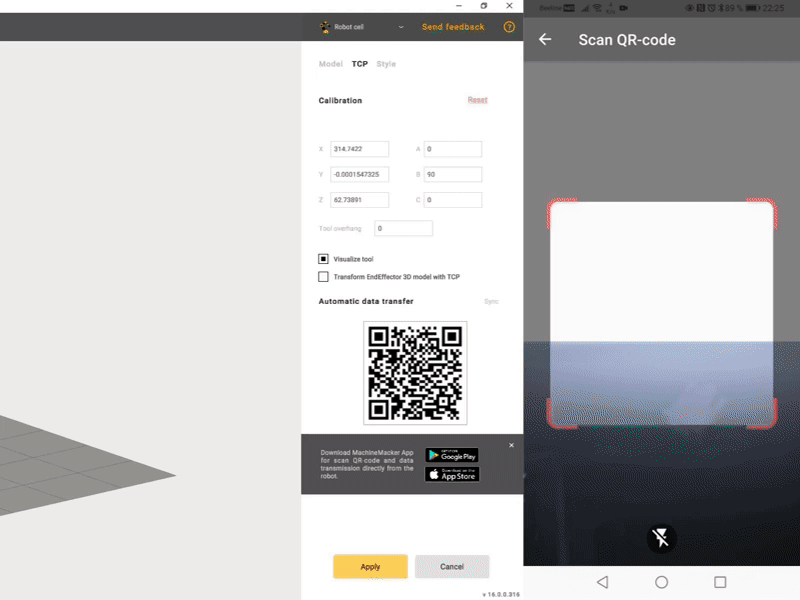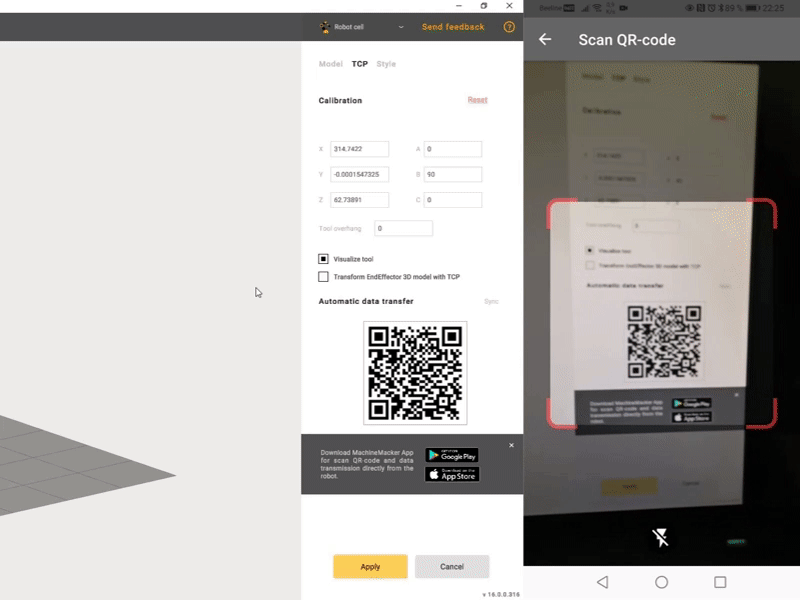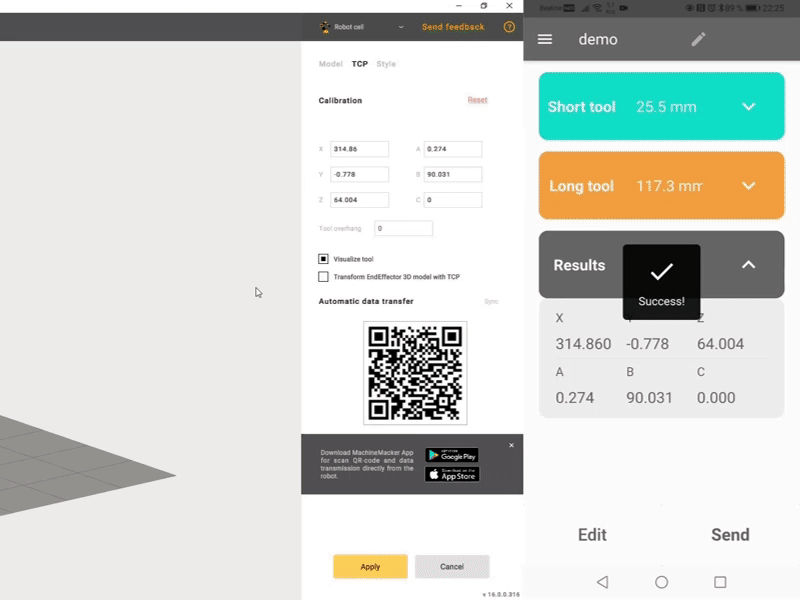
Measurement of the position of the long tool. The position of the tool is measured at different joint angles or at different positions along the robot path.

Step 2
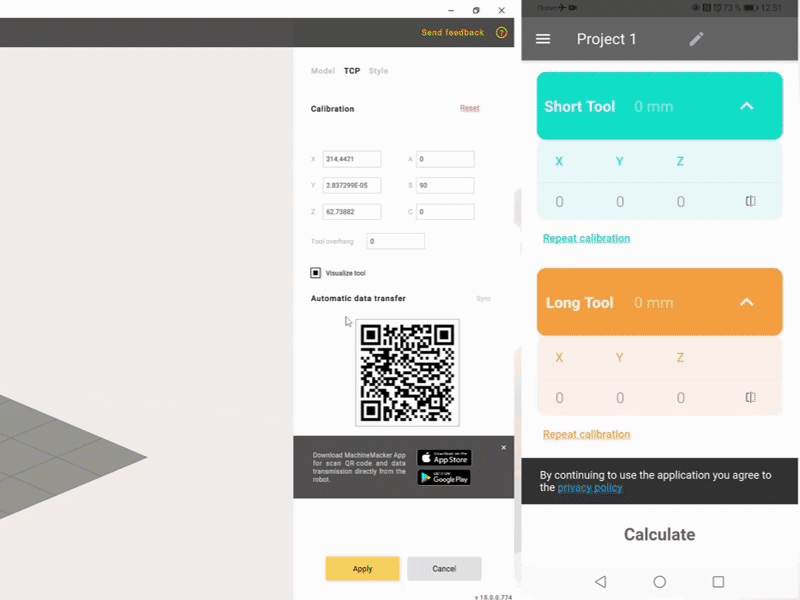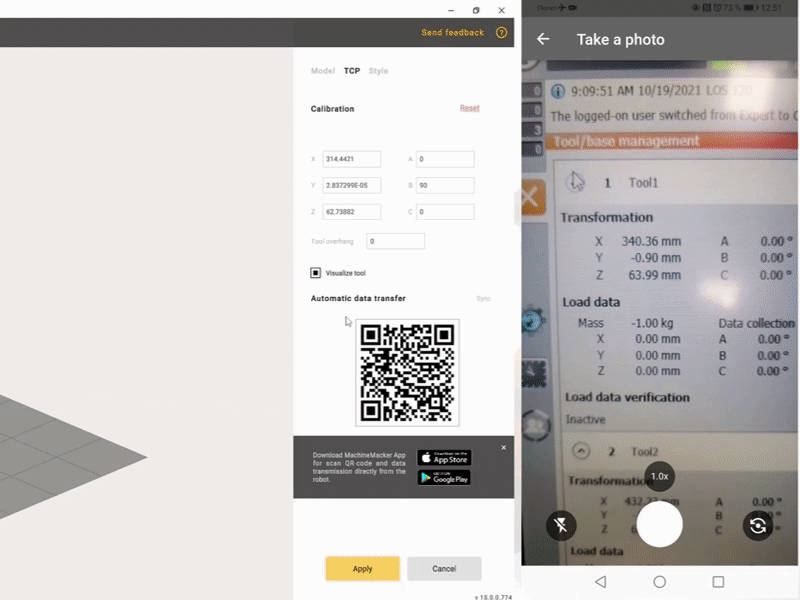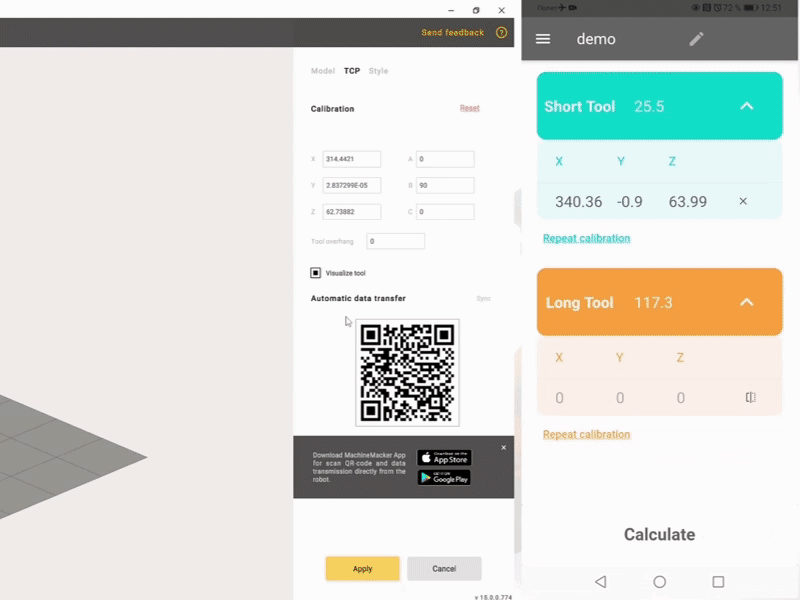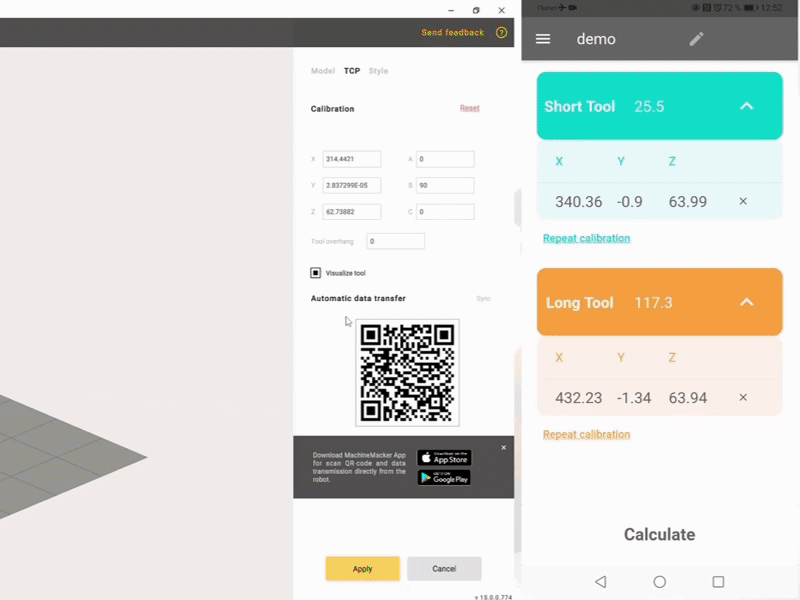
Measurement of the short tool position and automatic determination of the tool orientation.

Step 3
Automatic recognition with OCR and reading of the data by the Robot Calibration application and calculation of TCP coordinates.
Try Robot Calibration mobile app by SprutCAM Tech
Learn more
What is TCP calibration used for?
Tool Center Point (TCP) calibration is a process used in robotics to determine the position of a tool relative to the robot’s arm or body. This information is critical to ensuring the accuracy of the robot’s movements and the precision of its tool operations. The goal of TCP calibration is to find the exact position of the tool tip, which can then be used as a reference point for the robot’s motion control system. This allows the robot to consistently and accurately perform tasks such as cutting, drilling and welding in the correct location. The calibration process typically involves measuring the positions of various points on the tool and using these measurements to calculate the position of the TCP.
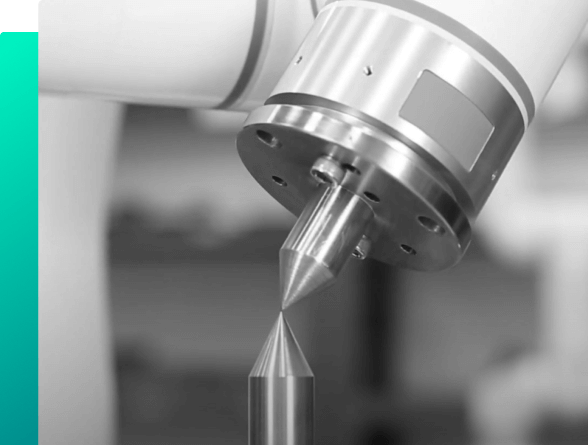


What is the double-spike method in TCP calibration?
The double-spike method is a tool center point (TCP) calibration method used in robotic and machine tool applications. It consists of measuring two points on a probe and calculating the position of the tool center point (TCP) based on these measurements. The purpose of TCP calibration is to determine the location of the TCP with respect to the robot’s base coordinate system so that it can be accurately positioned for machining or other operations. The double-spike method is one of several methods used for TCP calibration and can be useful in situations where the probe is unable to measure the tool position at the exact TCP.